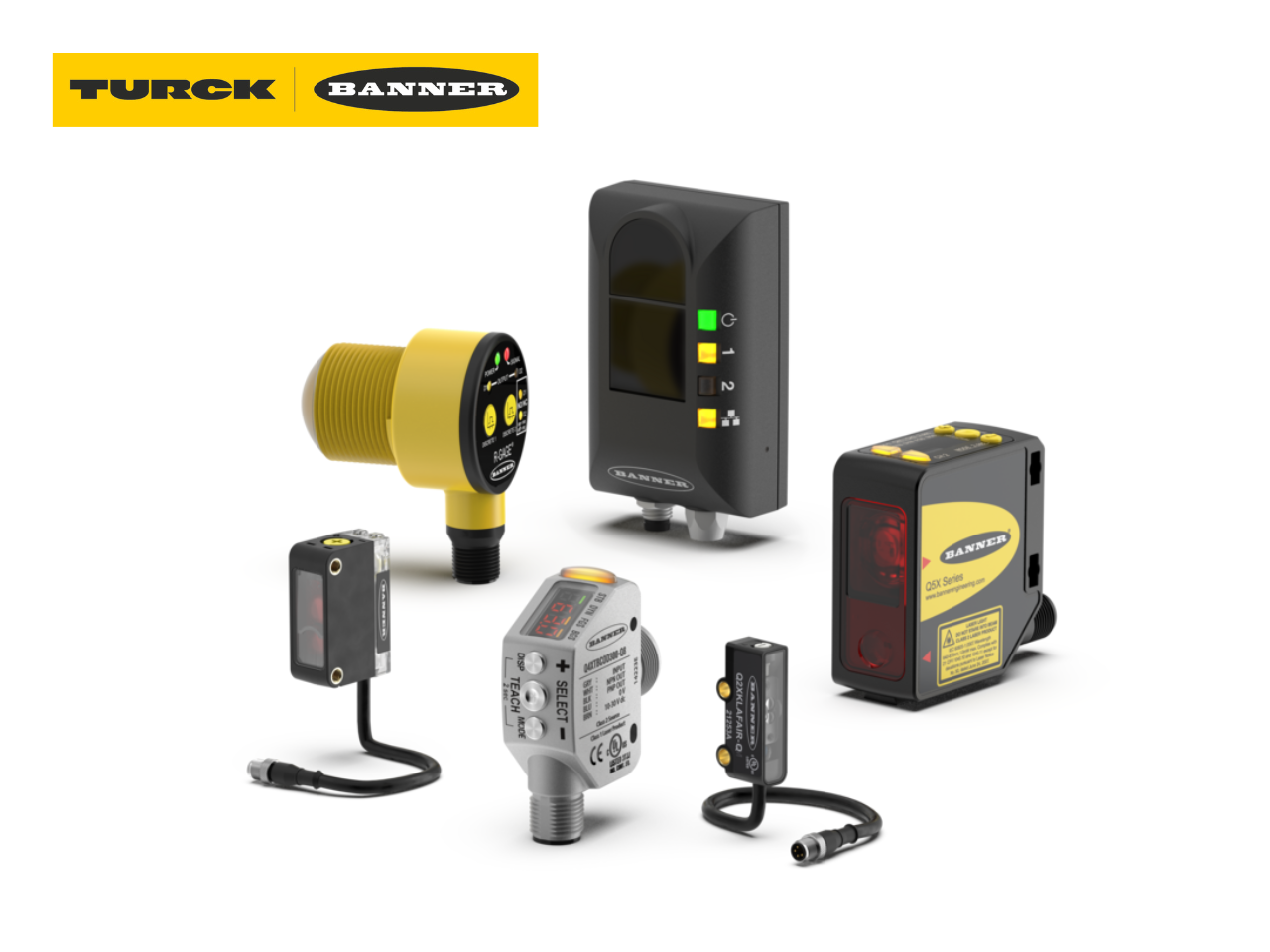
Since its inception in the 1980s, machine vision has concerned itself with two things: improving the power and capabilities of technology and making it easier to use. Today, machine vision is turning to higher-resolution cameras with higher intelligence to enable new automation solutions both inside and outside the factory – all simplifying access to smartphone, greatly reducing the technical requirements and associated costs.

And, just as in other industries that are benefiting from rapid advances in technology such as Big Data (big data), cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI) and mobile technology, developers Manufacturing, logistics and other businesses will also benefit from three key advances in machine vision for automation.
Sensor technology improves rapidly
While 1-, 2-, and 5-megapixel (MP) cameras continue to make up the majority of machine vision camera shipments, we’re seeing significant interest in higher resolution smart cameras , up to 12 MP. The high resolution sensor means that a single smart camera can do the job of several lower resolution smart cameras while maintaining high accuracy checks. .
Cognex’s patent-pending High Dynamic Range Plus (HDR+) image processing technology provides image fidelity even better than your regular HDR. It will help the smart camera check multiple areas on large objects where light uniformity is less than ideal. In the past, light variations could be mistaken for defects or even unseen features. Today, HDR+ helps reduce the impact of light variations, enabling application in challenging environments that were beyond the reach of machine vision technology just a few years ago.
While advanced smart cameras run HDR+ technology on field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to improve the quality of images captured at frame rates, additional sensor technology, such as such as time-of-flight (ToF) sensors, are being incorporated to enable “distance-based dynamic focus”. The new High Power Integrated Torch Imaging System (HPIT), which utilizes ToF distance measurement technology and high-speed liquid lens , is also making an impact by enabling dynamic autofocus at speed Frames. The latest barcode readers integrate HPIT capabilities for applications such as high-speed tunneling and warehouse management in situations where package and product sizes can vary significantly, requiring significant the camera must quickly adapt to different focal ranges.
Integration with Deep Learning
Just like the impact of AI in other industries, deep learning vision software for factory automation allows businesses to automate inspections that were previously only possible manually or resolved. more efficient than complex, cumbersome or time-consuming inspection challenges compared to traditional machine vision rules.
The biggest use of driving investment in deep learning is the potential to reallocate, in many cases, hundreds of human inspectors with deep learning-based inspection systems. For the first time, manufacturers have the technology to deliver inspection solutions that can achieve performance comparable to human technology.
One example of how deep learning can benefit organizations is defect detection testing. Every manufacturer wants to eliminate industrial defects as much as possible and as early as possible in the manufacturing process to reduce downstream impacts that cost time and money.
Defect detection is challenging because it is nearly impossible to account for the absolute amount of variation in the defect component or what anomalies may be within the acceptable range of variation. As a result, many manufacturers employ inspection personnel at the end of the process to perform a final inspection for unacceptable product defects. With deep learning, quality engineers can train a machine vision system to learn what is acceptable or unacceptable defect from a dataset of reference images instead of making program the visual system to account for thousands of defective possibilities.
Internet of Things
A key development for the smart camera vision system enabling Industry 4.0 initiatives is the Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture (OPC UA). With contributions from all the major machine vision trade associations in the world, OPC UA is an industry interoperability standard developed to help with machine-to-machine communication.
Combined with advanced sensor technology and trends like deep learning, OPC UA will help transform machine vision technology from a point-to-point solution to connecting the industrial world inside the factory and the physical world outside. beyond it. Today, vision systems and barcode readers are vital data sources for modern businesses.
Source: Cognex