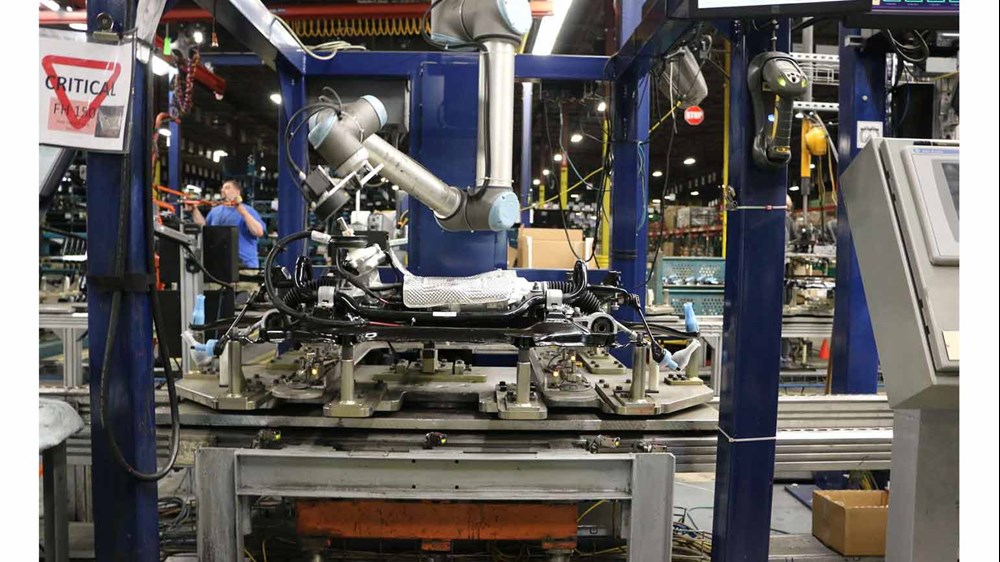
The automotive industry has been using industrial robots for more than half a century since General Motors first adopted UNIMATE in the early 1960s. During the transition period, a large number of robots were used in the auto sector. has experienced strong growth. Robotic technology has also improved with lower cost, more flexible, collaborative systems that have helped complement and replace bulky and inflexible traditional robots.
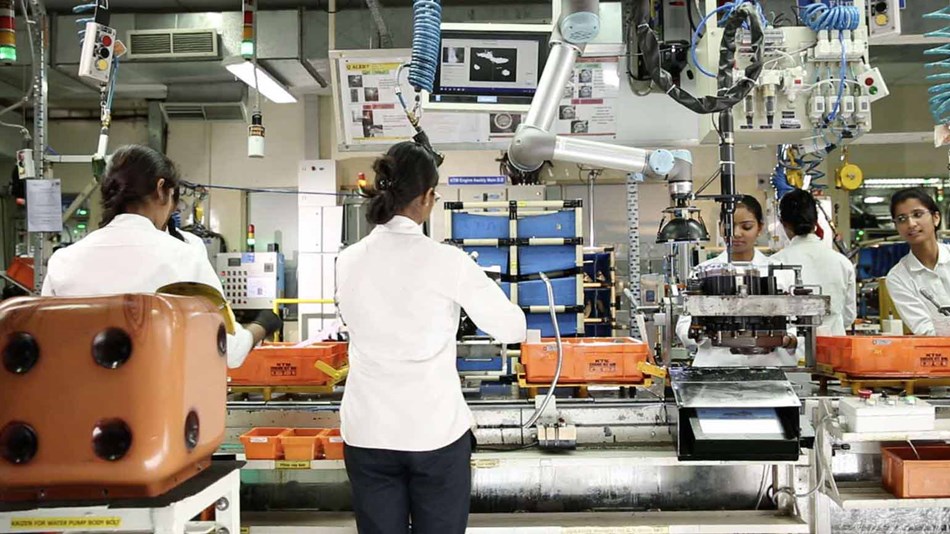
Using robots allows automakers and auto parts manufacturers to speed up production, reduce costs, improve quality, and protect workers from hazards. Collaborative robots (or “cobots”) have created new possibilities for automakers, including the ability to deploy robotic arms near workers without the need for fences. Cobots allow manufacturers to free workers from tedious, dirty and dangerous jobs – plus, the robotic arm is available 365 days, 24/7.
WHERE IS INDUSTRIAL ROBOT USE?
There are very few industries that are not reaping the benefits of automation. Since the first automotive robot entered the production line at GM, countless other factories and warehouses have adopted robotic technology. Industrial robots include the pharmaceutical, general manufacturing, medical and agricultural sectors. Universal Robots cobots are flexible platforms that can be deployed on multiple tasks in multiple environments. The only limits are the payload, safety compliance and your imagination.
WHAT ROOTS INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS RESPONSIBLE?
Applications of robots in manufacturing include a wide range of jobs from material handling; select & set; appraisal for assembly; Packing & unloading pallets and finishing. Robots are designed to perform repetitive tasks and free workers from strenuous physical work. Robots can be equipped with machine vision and artificial intelligence systems that allow them to react to a variety of situations and provide feedback on system performance in real time.
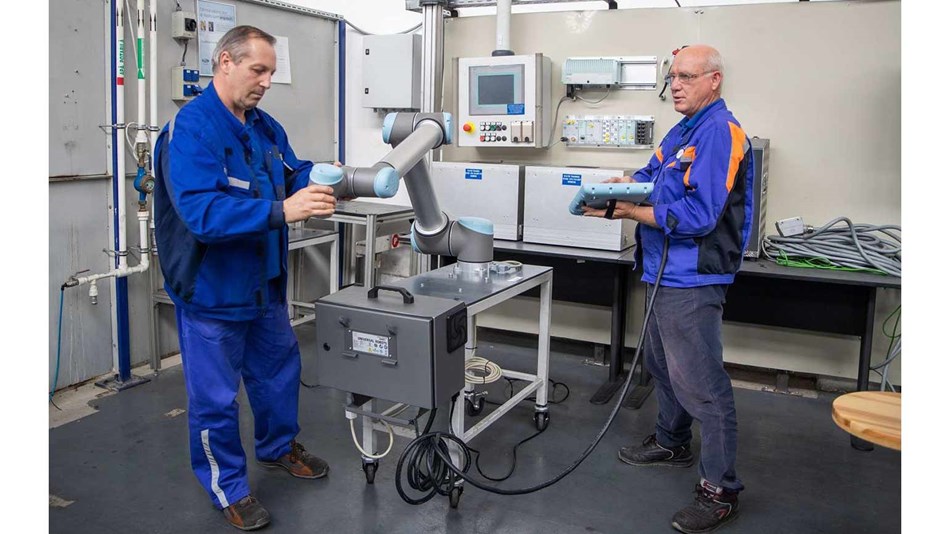
COBOT IN CAR MANUFACTURING
Some of the pressing problems faced by automotive assembly lines include the risk of injury, slow lead times, and end-product quality problems. These problems can be solved by deploying an automated robot.
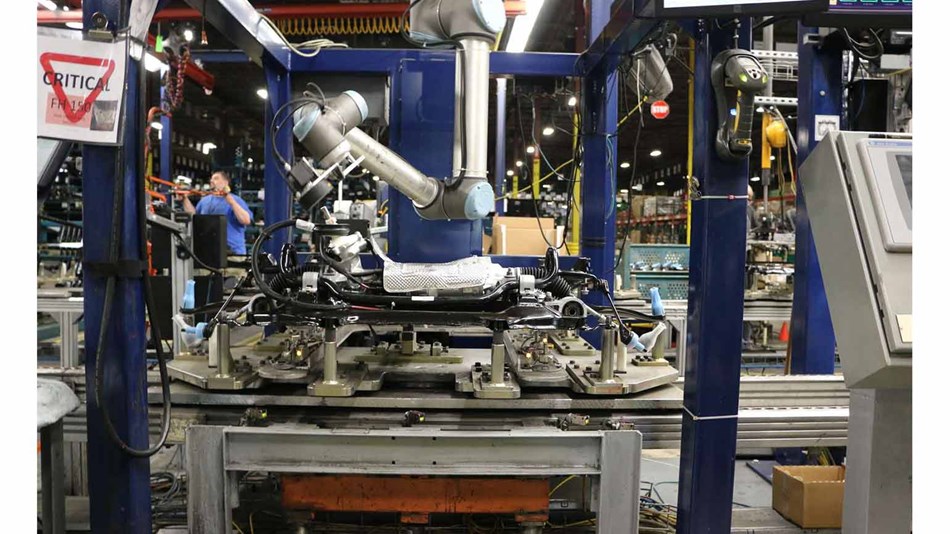
For example, the UR10 cobot is used by Continental in Spain, a leader in the automotive sector to perform tasks that handle and activate printed circuit boards and components during production.
Lear Corporation uses compact, flexible UR5 con cobots to assist in the assembly of car seats. The UR5 robotic arms are small (Ø 149 mm), allowing them to operate in tight spaces, where they can perform tasks such as assembling car seats and support frames. At Lear, the UR5 cobot completes screwdriving 8,500 times per day, which optimizes the company’s production time. Lear deployed its first UR robotic arm in 2017 – now, the company has 38 UR robots at its factory in China to perform car seat screw tightening, electrical testing, picking & placing and other important processes.
Paint
Paint robots have become an integral part of robotic car manufacturing. The robot delivers consistent paint performance and round-the-clock operation that no other worker can match. Moreover, car paint is toxic and dangerous to humans. Tasks like spraying a perfectly uniform coat of paint over a large surface are best handled by the robotic arm. The robot’s accuracy and efficiency in painting tasks also reduces production costs over time as less paint is wasted and there are no human errors.
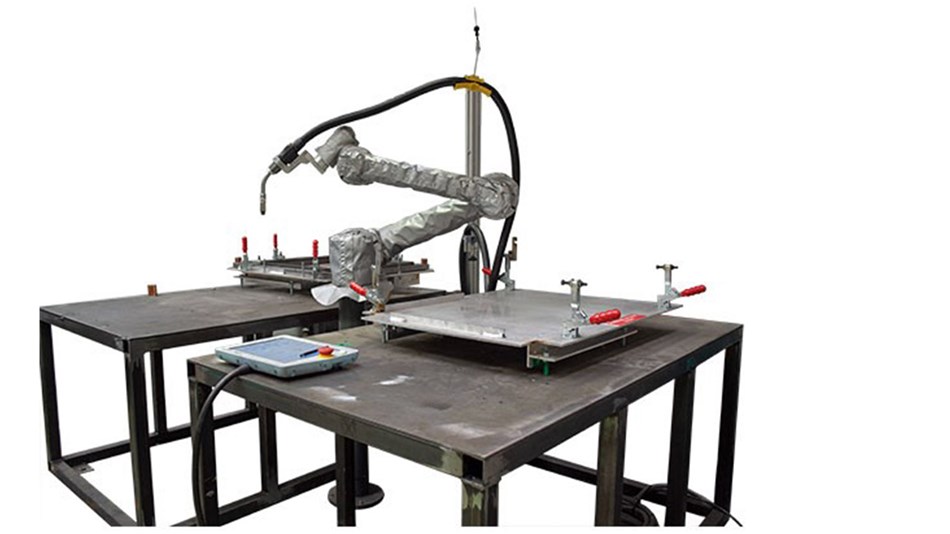
Welding robot
Welding is another dangerous and time-consuming job that is extremely suitable for cobots. Cobot can do arc, TIG, laser, MIG, ultrasonic, plasma and spot welding, as well as brazing and brazing. The UR+ platform provides all the hardware and software you need to get started with automotive welding applications. For example, the Olympus UR welding system is a low-cost welding solution perfectly suited for small auto parts manufacturers.
► Website: https://vuletech.com/
► LinkedIn: https://lnkd.in/e6rbG6e
► Youtube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCmHCn0T-oSbizOiWdYbRWzw